
ADHD is a neurological disorder that affects your ability to pay attention, maintain stillness, and control your behavior. It occurs in kids and teenagers and can last until maturity. It is the mental disorder in kids that is most frequently diagnosed. Compared to girls, boys are more likely to have it. It cannot be prevented or cured. A kid or adult with ADHD can manage their symptoms, though, if they are diagnosed early and have a strong treatment and education plan.
According to a study conducted by numerous Kenyan clinicians, the prevalence of ADHD cases has increased from 18% to 45%. The Vanderbilt Assessment Scale was one of many tests administered as part of the study to kids who had been transported to the hospital by their parents.
CAUSES OF ADHD
Current research indicates that genetics plays a significant role in ADHD, despite the fact that the cause(s) and risk factors are unknown. Researchers have also connected other aspects to it, such as brain injury, environmental risks, drug and substance usage when pregnant, etc.
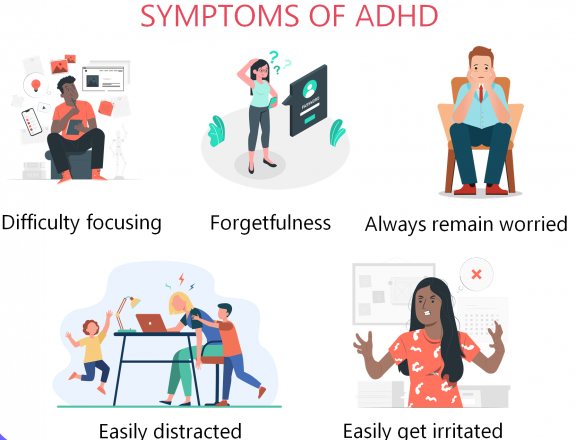
SYMPTOMS OF ADHD
ADHD is characterized by 3 core symptoms
- Inattentiveness: This condition is characterized by a person’s primary symptoms of forgetfulness, procrastination, distractibility, making mistakes or oversights that others may label as “careless,” and having trouble focusing during discussions, in class, and in other situations.
- Hyperactivity: A condition in which a person frequently exhibits signs of hyperactivity, such as fidgeting, restlessness, impulsivity, and blurting out thoughts in the middle of a conversation at a moment that others might find inappropriate.
- Impulsiveness: the inability to wait one’s time, continuously being on the go, and frequently interrupting others in discussion.
ADHD INTERVENTIONS IN KENYA
There are drug interventions and non-drug interventions in Kenya:
- Non-drug interventions
Making changes to the environment to support more fruitful social interactions is one of the non-drug treatments for ADHD. Among these modifications include adding more structure and promoting routines. Adults and children may respond differently to these therapies. Children’s interventions, for instance, can involve helping them tidy their belongings and make a timetable. Adult interventions could consist of coaching, behavioral therapy, and stress management.
- Drug interventions
These are the drugs that doctors have recommended for patients with ADHD. Together, the patient and the doctor will decide which drug is best for them, as well as the proper dosage and regimen. Finding the ideal combination could take some time.
Combining drug and non-drug interventions yields the best outcomes. The best treatments frequently combine medication, therapy, behavior modifications, and skill development. This is referred to as multimodal therapy.
CHALLENGES FACING PERSONS DIAGNOSED WITH ADHD
There are a number of of challenges facing persons with ADHD. Some may include:
- Lack of awareness on ADHD
There is insufficient information on ADHD. This results to stigma of persons with ADHD. Their behavior may sometimes be perceived as rude or unbecoming in social settings such as schools. For instance, children who live with ADHD would have issues with paying attention in class. As a result, they may go through a lot of punishments at school yet it is not their fault
- Lack of proper treatment
Healthcare workers may not be equipped with enough knowledge to diagnose and treat ADHD. As a result, many cases of ADHD will go misdiagnosed or not even diagnosed. Aside from that, there is an insufficient number of healthcare professionals who can diagnose and treat.
- Poverty
Treatment of ADHD might be quite expensive for the ordinary Kenyan. With high poverty rates and a high cost of living, a lot of persons diagnosed with ADHD may not be able to afford treatment. ADHD needs both drug and non-drug interventions. These drugs are not cheap. Therapy may also not be affordable.
- Lack of resources
One of the biggest challenges hindering mental health care in Kenya is the lack of resources. There isn’t enough allocation of resources made for mental health facilities. As a result, the little facilities may face stress from dealing with the rising number of mental health cases.
Those are some of the challenges facing persons diagnosed with ADHD.
CONCLUSION
As mentioned earlier, ADHD is on the rise in Kenya. This urgently calls for intervention. It is important as a society to come together and address this. Furthermore, as a country, we need to pay more attention to mental health.
