A child’s sensory control is determined by their sensory processing. Postural disorders in children with sensory processing disorders may show symptoms. This is due to the fact that these kids are less able to adjust to sensory perturbations since they are less sensitive to sensory input. When there are sensory conflicts, they display poorer postural stability.
A kid must be able to assume and maintain stable positions, move without losing balance, and have appropriate postural control to support movements of the hands and legs in order to effectively satisfy environmental demands. For a youngster to be competitive and successful in his or her performance areas, such as play, home, and school, this becomes crucial.
Children with Postural Disorder (PD) show weak core stability and limited endurance. As a result, they are frail, have little stamina, and frequently have poor balance. They frequently possess low body awareness and move inefficiently. The tactile (touch), proprioceptive (muscles and joints), and vestibular sensory systems are the most impacted.
Postural control is based on sensory input from the vestibular, proprioceptive, and tactile channels, which is then used by a feedback mechanism to produce corrective muscle responses to resist gravity. In this job, control does not rely equally on the three channels; rather, after a sensory integration, or reweighting process, input from each channel is weighted according to its relative reliability.

In order to make up for their diminished stability and poor body control, people with PD broaden the “platform” on which their bodies rest in order to increase their “base of support.” For instance, standing with legs shoulder width apart and lifting arms with bent elbows in a “basic” posture, as well as sitting in the “W-sit” position, both offer a wider base of support. Muscles that fire together naturally in the majority of people frequently do not activate with equal vigor in children with PD, causing them to feel unsteady, uneasy, and unsafe (e.g., quadriceps with hamstrings, abdominals with back muscles, biceps with triceps). It is known as poor muscle co-contraction among therapists.
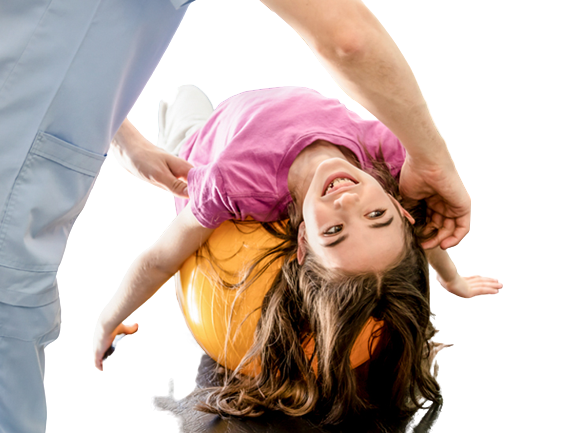

These postural abnormalities may be corrected with therapy. The program’s objectives are to:
- Strengthen weaker muscles
- Encourage maintaining good posture and raising awareness of
- Encourage individuals to maintain their ideal body posture and raise awareness of posture.
- Strengthening exercises for the main muscles affecting posture are also beneficial.
- Postural exercises should be performed until the person can maintain the proper posture without effort.
- The activities should be performed until the patient can walk and stand normally again.
We at Smart Sensory are keen on providing you with equipment needed for this therapy. You could contact us through our website at https://thesmartsensory.com/ or through our social media channels on Facebook, Instagram or LinkedIn.
